The Fascinating World of Plant Cells: A Journey Inside the Building Blocks of Life
Have you ever wondered what makes plants so different from animals? The answer lies within their cells! While both plant and animal cells share some similarities, they also have unique features that allow them to perform their vital functions. Let's embark on a journey inside the fascinating world of plant cells and discover the secrets that make them the foundation of life on Earth.
The Building Blocks of Life: A Closer Look at Plant Cells
Like all living things, plants are made up of tiny units called cells. These cells are the fundamental building blocks of life, and they perform all the essential tasks necessary for a plant to grow, thrive, and reproduce. Plant cells are eukaryotic, meaning they have a true nucleus that contains their genetic material (DNA). They also possess specialized structures called organelles, each with a specific role to play in the cell's overall function.
The Key Components of a Plant Cell: A Visual Guide
Let's take a closer look at the key components of a plant cell and understand their importance:
| Component | Function | Image |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Wall | Provides structural support and protection, giving the cell its rigid shape. |  |
| Cell Membrane | Controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell. | 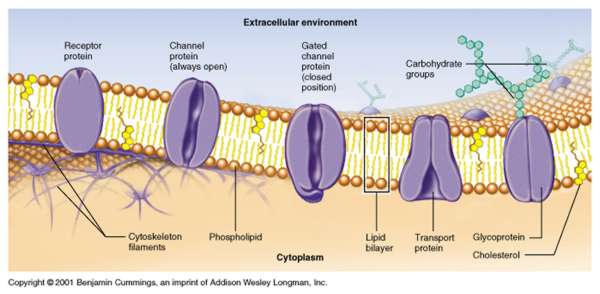 |
| Nucleus | Contains the cell's genetic material (DNA) and controls cellular activities. |  |
| Cytoplasm | A gel-like substance that fills the cell and contains organelles. |  |
| Ribosomes | Synthesize proteins, the building blocks of cells. |  |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) | A network of membranes involved in protein synthesis and lipid metabolism. |  |
| Golgi Apparatus | Processes and packages proteins for secretion. |  |
| Mitochondria | The powerhouse of the cell, responsible for cellular respiration and energy production. |  |
| Chloroplasts | Sites of photosynthesis, where plants convert sunlight into energy. |  |
| Vacuole | A large, fluid-filled sac that stores water, nutrients, and waste products. |  |
Unique Features of Plant Cells: What Makes Them Special?
Plant cells have several key features that distinguish them from animal cells:
- Cell Wall: This rigid outer layer provides structural support and protection, allowing plants to grow tall and stand upright. It's composed of cellulose, a complex carbohydrate that gives the cell wall its strength.
- Chloroplasts: These organelles contain chlorophyll, the green pigment that captures sunlight for photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy (sugars) that fuels their growth.
- Large Central Vacuole: This large, fluid-filled sac plays a crucial role in regulating water pressure within the cell, maintaining its shape, and storing nutrients and waste products.
The Importance of Plant Cells: The Foundation of Life
Plant cells are not only fascinating in their structure and function, but they also play a vital role in the ecosystem. They are the foundation of life on Earth, providing us with oxygen, food, and many other essential resources. By understanding the intricate workings of plant cells, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complex and interconnected nature of life.
Conclusion: A Journey of Discovery
Our journey inside the world of plant cells has revealed the intricate mechanisms that make these tiny structures the foundation of life on Earth. From the rigid cell wall to the chloroplasts that capture sunlight, each component plays a crucial role in the plant's survival and growth. As we continue to explore the wonders of the natural world, we gain a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of all living things and the importance of preserving our planet's biodiversity.


